Circle of life - our surfactants and the ecosystem
Among other things, surfactants from renewable raw materials are used, which are produced, for example, during the processing of maize (maize residues/biomass).
They are contained in the LeraFloor® products as emulsifiers on the one hand and as surface-active substances on the other and, in conjunction with equally sustainable complexing agents, serve to increase the dirt-carrying capacity.
This means that the dirt emulsifies (binds) with the surfactants and is held in the cleaning solution by the complexing agent. It is then removed gently but very effectively - without damaging the surface.
The use of natural and renewable raw materials supports ecological and agricultural plant cultivation worldwide.
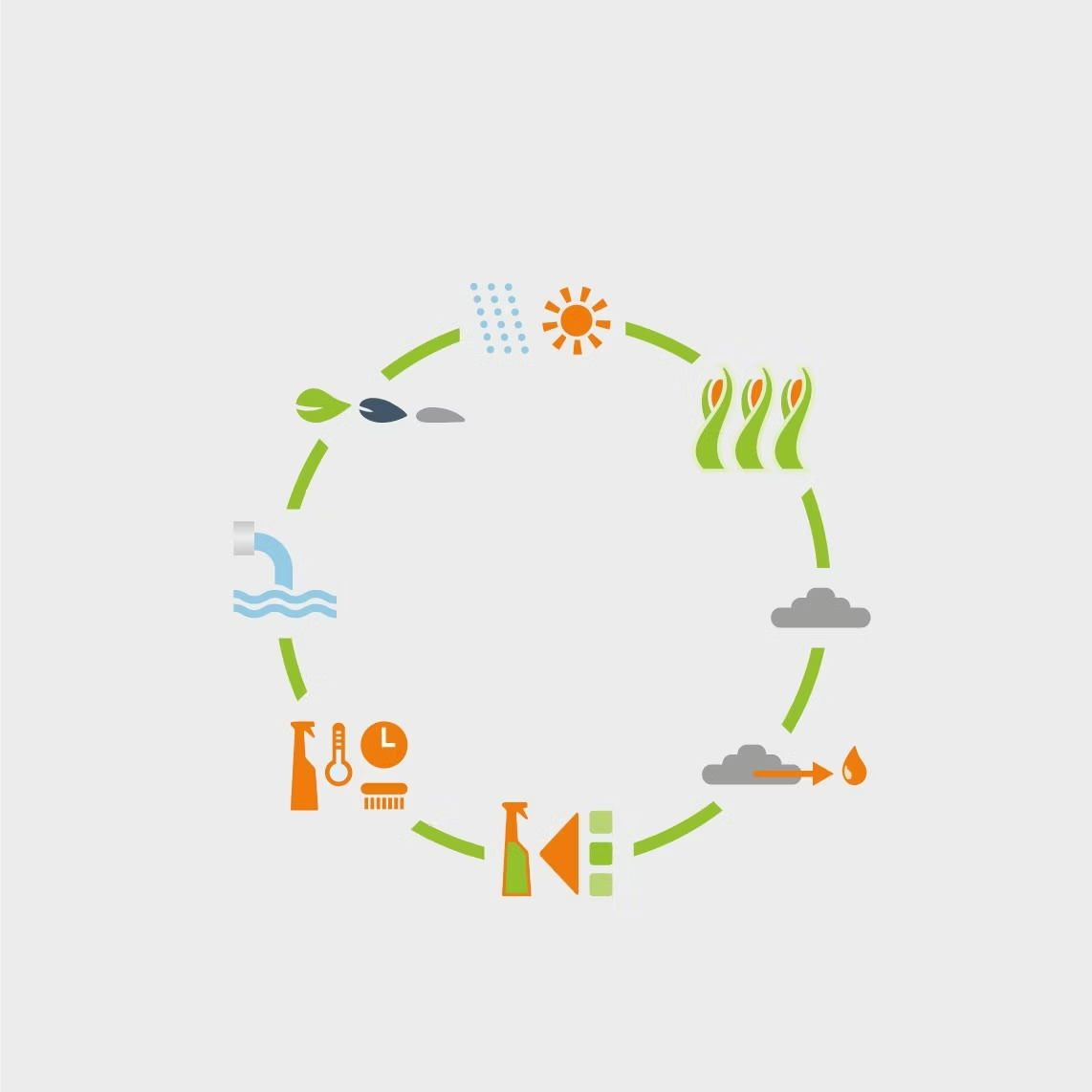
Natural drive
Solar radiation, CO2 and water are the natural drivers of the circular economy.
Renewable raw materials
We use maize plants and oils from sustainable plantations for our sugar surfactants.
Valuable biomass
is produced in the decomposition of the plants.
Extraction
of glucose, oils and fats.
Synthesis process
Conversion of fatty alcohols and glucose into an alkyl polyglycoside.
Cleaning
The surfactant is used for cleaning.
Waste water
The surfactants are decomposed in the sewage treatment plant at the latest.
Decomposition
What remains is water, CO2, minerals and biomass.
Natural drive
Solar radiation, CO2 and water are the natural drivers of the circular economy.
Renewable raw materials
We use maize plants and oils from sustainable plantations for our sugar surfactants.
Valuable biomass
is produced in the decomposition of the plants.
Extraction
of glucose, oils and fats.
Synthesis process
Conversion of fatty alcohols and glucose into an alkyl polyglycoside.
Cleaning
The surfactant is used for cleaning.
Waste water
The surfactants are decomposed in the sewage treatment plant at the latest.
Decomposition
What remains is water, CO2, minerals and biomass.
Product Benefits
Downloads
LeraFloor® assortment brochure
Service & Support
Our experts in Europe


